The number of companies using NPS® (Net Promoter Score) in customer experience management is rapidly increasing in Turkey.
What is NPS®?
NPS can be defined as a recommendation score measurement with a single question. It is a practical method that allows your customers to evaluate you with a single question instead of long and complicated survey questions. NPS® was developed by Fred Reichheld, Bain & Company and Satmetrix Systems. It was first announced by Reichheld in the article “One Number You Need To Grow” published in the Harvard Business Review in 2003.
How is the NPS calculation done?
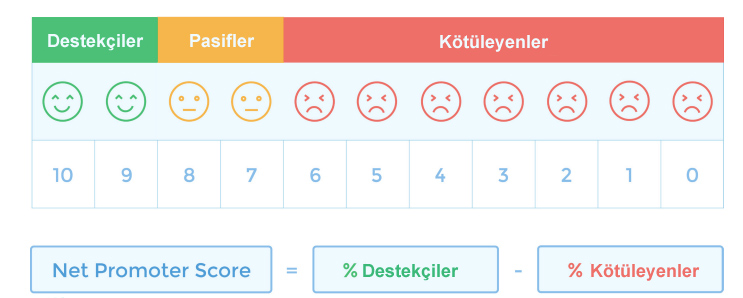
You ask your customers, “How likely are you to recommend us to your acquaintances? “ and ask for a recommendation score between 0 and 10.
Those who give 0-6 points are divided into the group that will not recommend you and will give you a bad reputation, while those who give 7 and 8 are not included in the calculation as a passive group that does not interfere with the calculation. 9 and 10 represent the supportive group who would recommend you.
The NPS is calculated by subtracting the percentage of detractors from the percentage of supporters out of the total respondents. The result of the NPS calculation is a score between -100 and +100.
Preference of Fortune 500 companies
NPS, which emerged in the early 2000s, quickly gained acceptance and became widespread. Today, almost all Fortune 500 companies regularly measure NPS. You can find the NPS results of the world’s leading companies in our related article.
The 6 most common mistakes in NPS measurement
NPS is preferred because it is a practical and popular method. We see that mistakes are often made in measurements made with the idea that everyone is doing it, so let’s do it too. Let’s look at the 6 most common mistakes together.
1- Asking the wrong question
The purpose of the NPS question should be to find out the likelihood of the customer you are asking about recommending your brand, service or product. Your question should be asked as “How likely are you to recommend us to your acquaintances?”.
If you want to measure NPS for your employees instead of customers, you should ask, “On a scale from zero to 10, how likely are you to recommend this company as a place to work?
Apart from the likelihood of recommendation, it is a mistake to ask how many points would you rate our products and services, how would you rate your satisfaction, etc.
2- Asking an NPS question to a customer with a problem
If you ask the NPS question to a customer who has encountered a problem and has not yet resolved it, they will probably give you a score between 0-6. The mood of a customer experiencing a problem is far from an objective assessment. Instead of asking a questionnaire to customers with an open or in-process request, it would be healthier to inform them about the solution of the problem. You can ask an NPS question during the first customer experience that the customer will have after solving the problem.
3- Asking a customer again in the same period
You can ask the NPS question to all your customers in certain periods. However, if the number of your customers is in the 6-7 digits, it would be more logical to create a sample and ask questions to the customers in the sample. For an accurate NPS result, a customer should not be asked the NPS question more than once in the same period. A customer’s score for NPS will not change daily or weekly. You can make a sample representing your customer profile or a breakdown of the customers offered products/services or a geographical grouping.
4- Colouring to guide the customer
The secret of the NPS lies in its scoring. When calculating the NPS, an arithmetic average is not taken from the scores given between 0-10. A percentage calculation is made in which those who give 0-6, 7-8 and 9-10 points are grouped. The customer dealing with the NPS question should not know this scoring and should not be guided. If you make a colouring as below, you will guide your customer.
5- Using more than one NPS question in a survey
Customer-facing NPS can be measured for brands, products and services. Suppose brand X has product Y and service Z. Our NPS questions could be as follows.
How likely are you to recommend brand X to your acquaintances?
How likely are you to recommend product Y to your acquaintances?
How likely are you to recommend service Z to your acquaintances?
You can ask these 3 questions at different times and in different surveys. However, if you ask these 3 questions together in the same survey, you may not get accurate results. The answers given can be affected by each other. Your customer can make a comparison and make an evaluation.
6- Customer experience management only with NPS
We said that NPS is popular and practical. However, it is not the right approach to call NPS a 100 percent accurate measurement and to do customer experience management only with NPS. There are many criticisms for NPS measurement. Consumer profiles in each country are different. There are cultural influences in the decision-making process. The rating criteria of an American consumer cannot be the same as that of a Turkish consumer. NPS is the result of research conducted in the USA. It may be accurate for the US, but it may not be as accurate for other countries.
Measure the NPS, but also measure the happiness score on the Likert scale, CSAT and other methodologies. Having other metrics to compare your NPS score to will minimise your margin of error.
Start calculating NPS now
Now you know the most common mistakes made during NPS measurement. But are you ready to start NPS measurement right away and measure instantly? Wiseback offers you the opportunity to measure NPS instantly. All you need to do is sign up for free and add the NPS component to your feedback survey. Start managing customer experiences in an end-to-end omni-channel structure.